Symptoms in infants
Infants suffering from angina may present the following symptoms:
- irritability and unusual crying ;
- difficulty feeding and drinking;
- moderate to high fever;
- redness inside the throat.
If your baby has these symptoms, or if you're concerned about his or her condition, consult one of our pediatricians for a full diagnosis.
Symptoms in children
In older children, angina is often easier to identify. The most common signs include
- difficulty swallowing, accompanied by pain ;
- fever (sometimes over 38.5°C);
- swollen, painful lymph nodes in the neck;
- the appearance of white patches or redness in the throat (white or red angina).
Viral or bacterial angina: what are the differences?
Viral angina is the most common form (80% of cases) in children, and disappears spontaneously in 3 or 4 days. The sore throat is often accompanied by :
- a runny nose (cold) or cough ;
- mouth ulcers;
- moderate fever.
Treatment: no antibiotics are required to treat viral angina. In general, rest and supportive care such as painkillers and good hydration are sufficient.
Bacterial angina, particularly streptococcal angina, is less frequent but requires special attention. It is characterized by :
- intense pain in the throat ;
- high fever ;
- an urge to vomit;
- no respiratory symptoms, such as coughing;
- white patches on the tonsils.
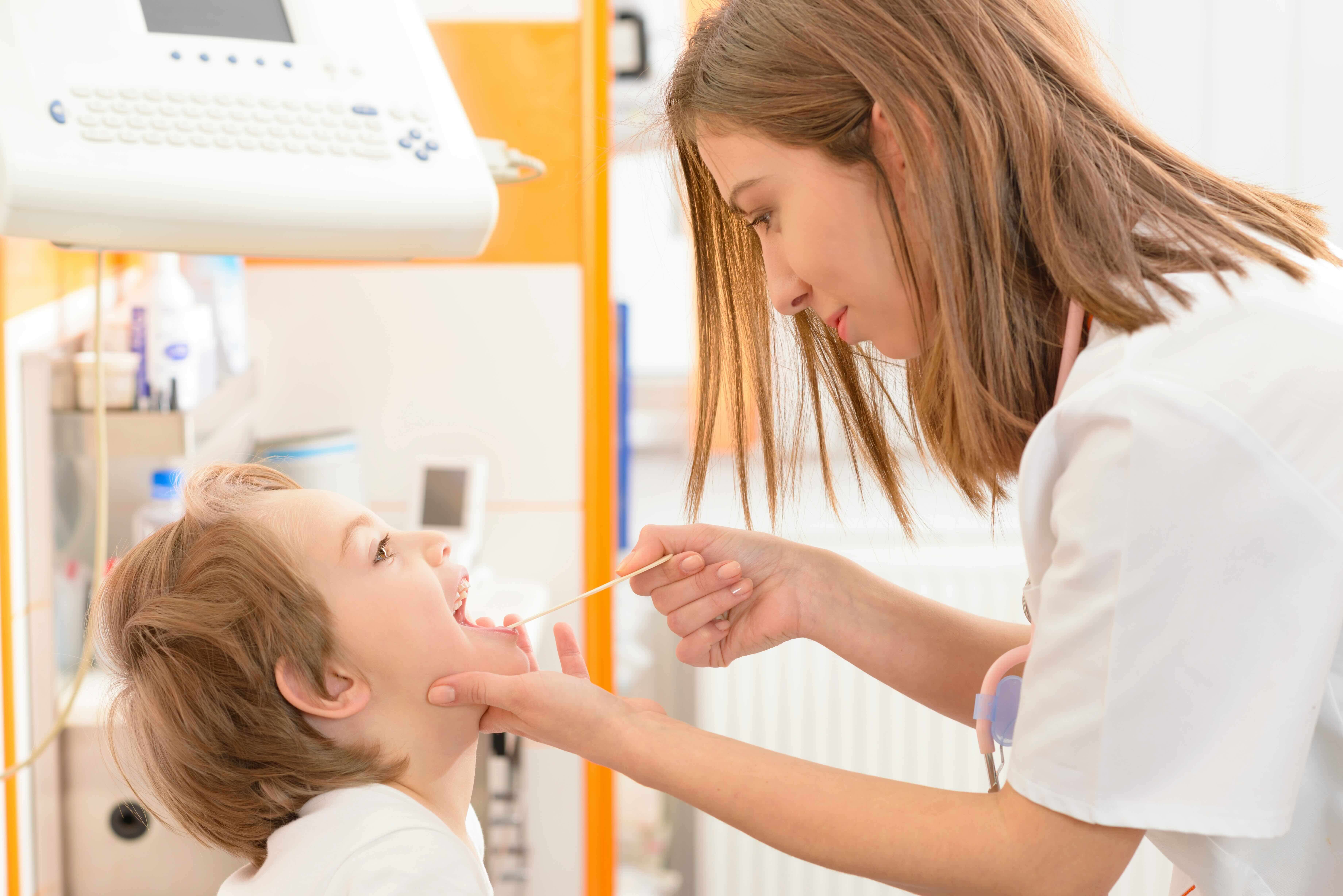
How is strep throat treated?
A throat smear is used to determine the presence of Group A Streptococcus, which causes bacterial angina. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe an antibiotic treatment, such as amoxicillin, which lasts between 7 and 10 days. Follow the treatment to the end, even if your child is feeling better. In general, a child with strep throat in good clinical condition can be treated without antibiotics, and recovers within a few days.
In addition, you can give your child painkillers such as paracetamol and antiseptic lozenges or sprays (if age-appropriate). Make sure your child eats fresh, easy-to-eat foods (compotes, purées, etc.) and drinks plenty of fluids (avoid hot, fizzy drinks) to soothe throat irritation.
Strep throat can also cause scarlet fever, a bacterial infection characterized by a reddish rash and high fever.
When should you contact the Doctor?
Consult a healthcare professional if your child :
- has a high fever (over 38.5°C) for more than 48 hours;
- shows signs of dehydration
- has difficulty breathing
- drools or swallows with difficulty
- does not open mouth completely;
- presents a worrying general condition.
Is angina contagious?
Yes, angina, whether viral or bacterial, is contagious. It is transmitted by direct contact with an infected person (coughing, sneezing) or by sharing contaminated objects such as cutlery or toys. To limit the spread of the disease, remember to wash your child's hands frequently, and clean any objects or surfaces likely to be contaminated.
If I have strep throat, can my child go to nursery or school?
Although contagious, viral angina is benign and disappears spontaneously after a few days. Consequently, there's no need to avoid nursery or school. As soon as the symptoms, particularly the fever, have disappeared and your child's condition permits, he or she can return to the nursery or school.
Angina pectoris: avoiding confusion
It's important not to confuse angina, a throat infection, with angina pectoris, a heart condition. If your child complains of chest pains, consult a cardiologist as soon as possible to rule out any heart problem.
Things to remember
Angina in children is a common and often benign condition, but may require prompt medical attention if dehydration or poor general health are present. Understanding the symptoms, knowing how to distinguish between the different types of angina and applying the right treatment will help ensure your child's optimum recovery.